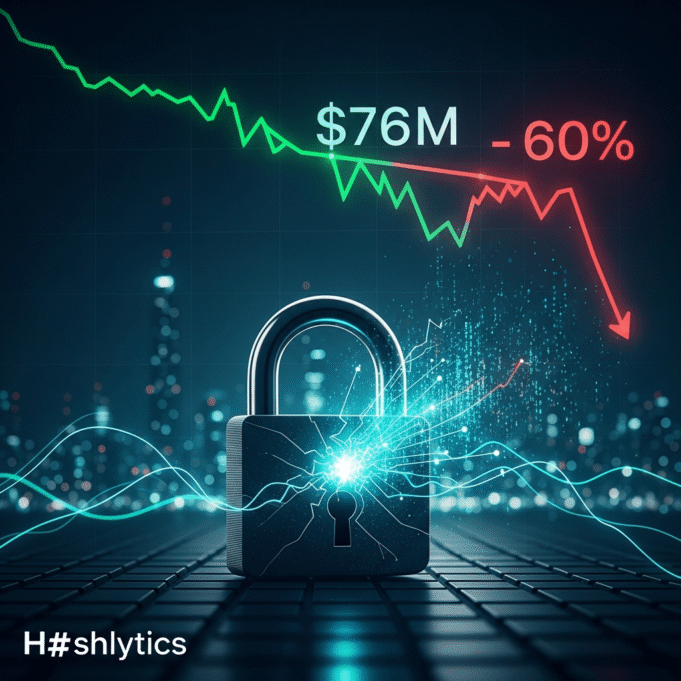
PeckShield reported on , that the crypto industry experienced $76 million in losses due to hacks and exploits during . This represents a 60% decrease compared to the $194.2 million in losses recorded in . The security firm identified 26 significant incidents during . Among the most substantial individual losses was a $50 million incident stemming from an address poisoning scam, which affected a single user. Additionally, a private key leak led to the compromise of a multi-signature wallet, resulting in a loss of approximately $27.3 million. Other notable attacks included the Trust Wallet browser extension exploit, which drained $7 million in user funds, and a $3.9 million hack targeting the Flow protocol.
The incidents underscore prevalent attack vectors in the crypto space. Address poisoning, responsible for the largest single loss of $50 million, involves threat actors sending small amounts of cryptocurrency from a wallet that closely resembles a legitimate address. The intent is to trick the victim into accidentally sending funds to the fraudulent address by exploiting human error, particularly when users quickly glance at or copy addresses from transaction histories. Browser-based wallets, such as the Trust Wallet extension, present continuous online connectivity, which can increase their susceptibility to specific cybersecurity threats. The Trust Wallet exploit, specifically affecting version 2.68 of its Chrome extension, involved a malicious code update that exfiltrated wallet data and drained funds. Overall, saw crypto theft reach an estimated $3.3 billion to $3.4 billion across over 300 major incidents, with the average loss per event more than doubling from approximately $5 million to nearly $15 million, indicating a shift towards high-value targets and organized criminal activity.
The reported incidents in primarily resulted from exploits that capitalized on both technical vulnerabilities and human factors. Address poisoning attacks leverage the visual similarity of wallet addresses and users’ reliance on transaction history, preying on carelessness and haste. The Trust Wallet breach was attributed to a supply-chain attack via a malicious JavaScript file in its browser extension, highlighting the risks associated with browser-based applications that can be tricked into signing malicious transactions. The Flow protocol incident, along with the $27.3 million private key leak, points to vulnerabilities in multi-signature wallet security and key management practices.
While Trust Wallet has committed to fully reimbursing affected users, the specific timeline and finalized workflow for this reimbursement process remain unannounced. Further detailed information regarding the exact technical exploit for the $3.9 million Flow protocol hack beyond a multi-signature wallet compromise has not been fully disclosed.
Despite the decrease in overall losses for , the crypto industry continues to face evolving threats. As CryptoSlate reports, the combination of AI-driven social engineering, supply chain poisoning, and industrial-scale hacking necessitates continuous vigilance for capital preservation. Trust Wallet has urged users to update their browser extension to version 2.69 to mitigate further exposure and confirmed that its mobile applications were not affected. The ongoing nature of these sophisticated attacks suggests that security measures will need to adapt to protect digital assets.
To reduce exposure to common crypto exploits, users are advised to implement several safety measures. Firstly, always thoroughly verify the entire wallet address for every transaction, rather than relying on quick glances or transaction history, to counter address poisoning scams. Secondly, consider using hardware wallets, which are offline storage devices, for storing private keys to significantly enhance security against online threats. Thirdly, ensure all crypto wallet software and browser extensions are consistently updated to their latest versions, as updates often include critical security patches. Finally, remain vigilant against phishing attempts and only download extensions from official websites or verified sources, checking developer credentials and user reviews.
Follow us on Bluesky , LinkedIn , and X to Get Instant Updates