Microsoft announced February 2026 as the target year for mainstream adoption of Copilot+ PCs, a new category of Windows 11 computers featuring dedicated Neural Processing Units (NPUs) for on-device AI processing. The platform introduces Windows Recall, an AI feature that continuously captures screen snapshots to create a searchable visual history of user activity.
NPU Hardware Requirements
Copilot+ PCs require CPUs with integrated NPUs capable of at least 40 TOPS (trillion operations per second) of AI performance. Intel’s Lunar Lake processors, Qualcomm’s Snapdragon X Elite chips, and AMD’s Ryzen AI 300 series meet this threshold. The NPU handles AI workloads separately from the CPU and GPU, enabling efficient local AI processing without draining battery or affecting general performance.
Existing PCs, including recent models from 2023-2024, cannot be upgraded to Copilot+ status as the NPU must be integrated at the silicon level. Microsoft estimates that by end of 2026, approximately 50 million Copilot+ PCs will be in circulation as manufacturers transition their product lines.
Windows Recall Functionality
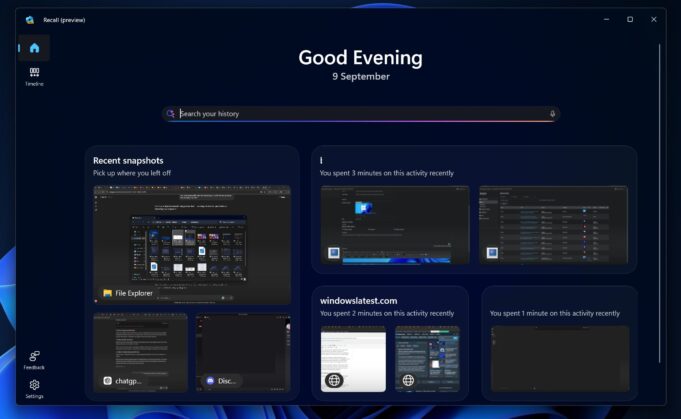
Recall captures screenshots every few seconds and uses on-device optical character recognition (OCR) and image analysis to index content. Users can search their activity history using natural language queries like “find that email about project deadlines” or “show me the recipe I looked at last week.” The system stores encrypted snapshots locally on the device rather than uploading to cloud servers.
Microsoft initially planned Recall as an opt-out feature but reversed course after security researchers demonstrated vulnerabilities in the storage implementation. The updated version, announced in October 2025, requires users to explicitly enable Recall through Windows Settings and implements additional encryption using Windows Hello authentication before accessing the snapshot database.
Privacy and Security Concerns
Security researchers at Cyber Security firm Doubleagent discovered that Recall’s original database implementation stored screenshots in plaintext SQLite files accessible to any process running under the user’s account. This would allow malware to exfiltrate the entire visual history without requiring elevated privileges. Microsoft responded by adding per-user encryption and requiring biometric authentication before Recall data can be accessed.
Privacy advocates have raised concerns about the feature’s potential for capturing sensitive information including passwords, financial data, and private communications even when users believe they’ve navigated away from those screens. Microsoft states that Recall excludes InPrivate browsing sessions and DRM-protected content, but critics note the system cannot distinguish between sensitive and non-sensitive information in regular application windows.
Competition with Apple Intelligence
The Copilot+ platform positions Microsoft against Apple Intelligence, announced in June 2025 for macOS Sequoia and iOS 18. Apple’s approach uses on-device processing for most AI tasks but offloads complex operations to “Private Cloud Compute” servers running on Apple silicon with cryptographic attestation that user data is not retained.
Microsoft’s architecture keeps more processing on-device but faces skepticism about privacy protections following Recall’s troubled debut. Apple has emphasized that its AI features don’t create persistent visual records of user activity, instead processing information only when explicitly requested by the user through Siri or system-level features.
Additional Copilot+ Features
Beyond Recall, Copilot+ PCs include Studio Effects for AI-powered video enhancement during calls (background blur, eye contact correction, voice focus), Live Captions with real-time translation for 40+ languages, and Cocreator for AI-assisted image generation in Paint. These features leverage the NPU to run locally without requiring cloud connectivity.
Microsoft’s integrated Copilot assistant provides context-aware help across Windows applications, though this functionality also works on standard Windows 11 PCs by routing requests to cloud servers rather than processing locally.
Market Positioning
Microsoft positions Copilot+ PCs as delivering performance comparable to systems five years older when running AI workloads, though independent benchmarks have not yet validated these claims broadly. The company partners with OEMs including Dell, HP, Lenovo, and ASUS to launch Copilot+ devices across price points from $999 to premium configurations exceeding $2,500.
Industry analysts note that mainstream adoption depends on demonstrating clear productivity benefits that justify new hardware purchases, particularly as many users upgraded during the pandemic and may not be in typical replacement cycles. The success of Windows 11’s AI features will likely determine whether NPU-equipped PCs become standard or remain a premium category similar to early touchscreen laptops.
Follow us on Bluesky , LinkedIn , and X to Get Instant Updates