Let’s face it: wrangling data is rarely a picnic. But what if you could harness the power of AI to make the process smoother, faster, and even…fun? This isn’t science fiction; it’s the reality of AI-powered data analysis. However, like any powerful tool, AI requires careful handling. This guide focuses on maximizing your AI data analysis efficiency, especially when using the ubiquitous CSV format.
AI Data Analysis: Critical CSV Tips & Tricks
Why CSV? Simple: smaller file size means less chance of hitting those pesky AI processing limits. Plus, the single-sheet structure eliminates ambiguity – the AI knows exactly where to look. Converting from XLSX or ODS? Just open your spreadsheet in Excel or Google Sheets, select the relevant sheet, and useFile > Save As…to save it as a CSV. You’ll lose data from other sheets, but that’s fine; we’re focused on one sheet at a time.
Choosing the Right AI Model: It’s Not Just About Power
Each AI platform offers a range of models.
Google’s Gemini (check out their model options here), for example, defaults to 2.5 Flash, but 2.5 Pro is better suited for “Reasoning, maths and code.”
Claude’s (model selection guide) and OpenAI’s Cookbook (model selection guide) offer excellent resources for understanding model differences. Even GPT-5 (which auto-selects models) benefits from well-crafted prompts to guide its choice. Remember: a less powerful model can often be faster, cheaper, and more environmentally friendly (learn more about the environmental impact).
Prompt Engineering: Talking to Your AI Effectively
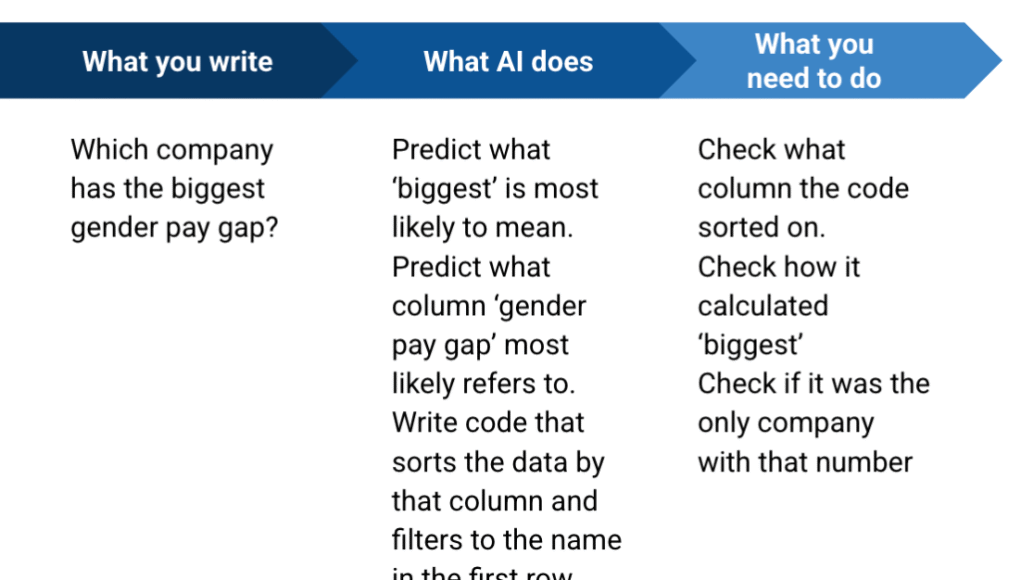
AI interprets your words probabilistically, leading to potential misinterpretations. Be explicit! Instead of “Count the total fires,” try “Use the ‘Incidents’ column to calculate the total number of fires.” Similarly, specify functions: “Calculate the median value for the ‘PatientTotal’ column,” not just “calculate the average.”
Consider breaking down complex calculations into steps. For example, a prompt might specify: “Here is data… I want you to calculate how many companies are in Birmingham. Use the ‘Address’ and ‘Postcode’ columns… [detailed instructions follow].”
Beyond Single Figures: Context is King
Don’t just ask for the “biggest” category; ask for the top 10 and bottom 10. This reveals outliers and provides a richer understanding. Similarly, request multiple averages (mean, median, mode) for a complete picture. Always ask for statistical summaries (min, max, quartiles, standard deviation) to understand data distribution.
Advanced Prompting Techniques: Outsmarting the AI’s Eagerness to Please

AI models are helpful, but not necessarily critical. Use prompt engineering to ensure accuracy. Meta-prompting (asking the AI to suggest prompts), role-playing (defining the AI’s role as a skeptical analyst), N-shot prompting (providing examples), recursive prompting (iterative refinement), negative prompting (specifying what NOT to do), and structured output prompting (specifying the desired output format) all help to refine your results.
Chain of Thought (CoT) and Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG): The Power of Structure and Context

CoT involves outlining analytical steps, forcing you to think critically about the process. The Inverted Pyramid of Data Journalism (updated model here) provides a useful framework. RAG enhances prompts with relevant context, such as methodologies, data dictionaries, or previous reports. Think of it as giving your AI a research assistant!
Context Windows and Conversation Limits

AI has memory limits. To avoid hitting them, summarize previous interactions before starting new ones. Break down complex analyses into smaller tasks, each handled in a separate conversation. Regularly download your results to check against the original data.
Finally, use adversarial prompting to challenge your assumptions and identify potential biases. Ask the AI to act as a skeptical editor, scrutinizing your methods and identifying potential flaws.
Ready to unleash the power of AI on your data? Let’s hear your tips and tricks in the comments below or on