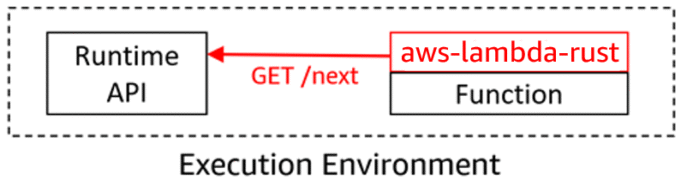
Why Rust for AWS Lambda?
| Advantage | Impact on Lambda |
|---|---|
| High Performance | Faster execution times reduce costs and improve latency |
| Memory Safety | Eliminates entire classes of bugs without garbage collection overhead |
| Zero-Cost Abstractions | High-level code compiles to efficient machine code |
| Small Binary Size | Faster cold starts and reduced deployment times |
Tooling: Cargo Lambda
Cargo Lambda is an open-source extension to the Cargo build system that simplifies building, testing, and deploying Rust-based Lambda functions.
Installation
curl -fsSL https://cargo-lambda.info/install.sh | shQuick Start: HTTP Lambda Function
Step 1: Create New Project
cargo lambda new hi_apiWhen prompted, answer “y” to create an HTTP function.
Step 2: Project Structure
This generates the following structure:
├── Cargo.toml
├── README.md
└── src
├── http_handler.rs
└── main.rsFile Roles
- main.rs: Sets up the Lambda runtime and connects to the handler function
- http_handler.rs: Contains the core function logic executed upon invocation
Step 3: Review Generated Code
main.rs:
use lambda_http::{run, service_fn, tracing, Error};
mod http_handler;
use http_handler::function_handler;
#[tokio::main]
async fn main() -> Result<(), Error> {
tracing::init_default_subscriber();
run(service_fn(function_handler)).await
}http_handler.rs:
use lambda_http::{Body, Error, Request, RequestExt, Response};
pub(crate) async fn function_handler(event: Request) -> Result<Response<Body>, Error> {
// Extract query parameter
let who = event
.query_string_parameters_ref()
.and_then(|params| params.first("name"))
.unwrap_or("world");
let message = format!("Hello {who}, this is an AWS Lambda HTTP request");
// Build and return HTTP response
let resp = Response::builder()
.status(200)
.header("content-type", "text/html")
.body(message.into())
.map_err(Box::new)?;
Ok(resp)
}Step 4: Local Testing
Before deploying, use Cargo Lambda to emulate the Lambda environment locally:
cargo lambda watchThis starts a local server for testing and debugging your function.
Step 5: Deploy to AWS
cargo lambda deployStep 6: Invoke Remotely
cargo lambda invoke --remote hi_api --data-file payload.jsonAdvanced: AWS CDK Integration
For complex deployments, the AWS Cloud Development Kit (CDK) simplifies integrating Rust Lambda functions into infrastructure-as-code stacks. The AWS CDK allows infrastructure definition in languages like TypeScript, providing type safety and maintainability.
Why Use AWS CDK?
- Infrastructure as Code: Define infrastructure alongside application code
- Type Safety: Catch configuration errors at compile time
- Reusable Constructs: Create modular, composable infrastructure components
- Multi-Resource Management: Coordinate Lambda, API Gateway, databases, and more
CDK Setup: Step-by-Step
1. Create CDK Project
mkdir rusty_cdk
cd rusty_cdk
cdk init --language=typescript2. Install Cargo Lambda CDK Construct
npm i cargo-lambda-cdk3. Create Rust Lambda Function
mkdir lambda
cd lambda
cargo lambda new helloRust4. Update CDK Stack
Edit lib/rusty_cdk-stack.ts:
import * as cdk from 'aws-cdk-lib';
import { HttpApi } from 'aws-cdk-lib/aws-apigatewayv2';
import { HttpLambdaIntegration } from 'aws-cdk-lib/aws-apigatewayv2-integrations';
import { HttpMethod } from 'aws-cdk-lib/aws-events';
import { RustFunction } from 'cargo-lambda-cdk';
import { Construct } from 'constructs';
export class RustyCdkStack extends cdk.Stack {
constructor(scope: Construct, id: string, props?: cdk.StackProps) {
super(scope, id, props);
// Define Rust Lambda function
const helloRust = new RustFunction(this, 'helloRust', {
manifestPath: './lambda/helloRust',
runtime: 'provided.al2023',
timeout: cdk.Duration.seconds(30),
});
// Create HTTP API Gateway
const api = new HttpApi(this, 'rustyApi');
// Create Lambda integration
const helloInteg = new HttpLambdaIntegration('helloInteg', helloRust);
// Add route
api.addRoutes({
path: '/hello',
methods: [HttpMethod.GET],
integration: helloInteg,
});
// Output API URL
new cdk.CfnOutput(this, 'apiUrl', {
description: 'The URL of the API Gateway',
value: `https://${api.apiId}.execute-api.${this.region}.amazonaws.com`,
});
}
}5. Bootstrap CDK (First-Time Setup)
cdk bootstrapThis only needs to be run once per AWS account/region combination.
6. Deploy Stack
cdk deployArchitecture Overview
CDK Deployment Stack
┌─────────────────────────────────────┐
│ AWS CDK Stack (TypeScript) │
│ │
│ ┌──────────────────────────────┐ │
│ │ RustFunction Construct │ │
│ │ (cargo-lambda-cdk) │ │
│ │ │ │
│ │ - Builds Rust code │ │
│ │ - Creates Lambda function │ │
│ │ - Configures runtime │ │
│ └──────────────────────────────┘ │
│ │ │
│ ▼ │
│ ┌──────────────────────────────┐ │
│ │ HTTP API Gateway │ │
│ │ │ │
│ │ - Routes: /hello │ │
│ │ - Methods: GET │ │
│ └──────────────────────────────┘ │
│ │ │
│ ▼ │
│ ┌──────────────────────────────┐ │
│ │ Lambda Function │ │
│ │ (Rust compiled binary) │ │
│ └──────────────────────────────┘ │
└─────────────────────────────────────┘Comparison: Cargo Lambda vs CDK Approach
| Aspect | Cargo Lambda | AWS CDK |
|---|---|---|
| Best For | Simple, single-function deployments | Complex, multi-resource infrastructure |
| Setup Complexity | Minimal (Rust only) | Moderate (Rust + TypeScript/Python) |
| Infrastructure Control | Limited (function-level only) | Complete (multi-resource orchestration) |
| Local Testing | Built-in with cargo lambda watch |
Requires additional setup |
| Team Collaboration | Good for Rust teams | Better for cross-functional teams |
Key Takeaways
General Availability Significance:
- Production SLA: AWS now provides service level agreements for Rust Lambda functions
- Enterprise Readiness: Official support makes Rust viable for mission-critical workloads
- Performance Benefits: Rust’s efficiency translates to cost savings and improved latency
- Memory Safety: Eliminates entire classes of bugs without garbage collection overhead
- Ecosystem Maturity: Cargo Lambda and CDK integration streamline development workflows
When to Choose Each Approach:
- Use Cargo Lambda: Quick prototypes, single-function microservices, Rust-focused teams
- Use AWS CDK: Multi-service applications, complex infrastructure, cross-functional teams, reusable infrastructure patterns
The general availability of Rust support in AWS Lambda, combined with Cargo Lambda and AWS CDK tooling, represents a significant advancement for serverless development. Rust’s performance, safety, and zero-cost abstractions make it exceptionally well-suited for building scalable, reliable, and cost-effective cloud applications. This combination is expected to drive innovation in cloud computing as teams adopt Rust for production serverless workloads.