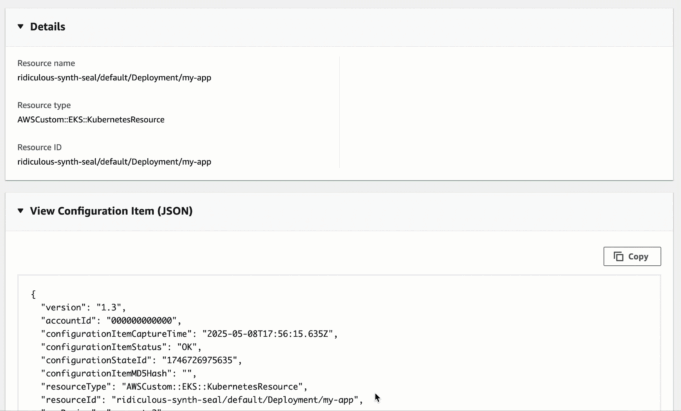
Why Use AWS Config for Kubernetes?
Imagine ensuring all your Deployments have at least two replicas for high availability, or verifying that all Pods use images from approved registries for security. AWS Config rules make these scenarios a breeze! With proper configuration, you can monitor and enforce compliance across your entire Kubernetes infrastructure.
Setting Up AWS Config for EKS
AWS CloudFormation provides an automated way to deploy AWS Config monitoring for your EKS clusters. By configuring the appropriate resource types and namespaces, you can start tracking your Kubernetes resources alongside your traditional AWS resources.
Querying Kubernetes Resources
Once configured, you can use advanced SQL queries to find specific resources across your clusters:
SELECT *
WHERE resourceType = 'AWSCustom::EKS::KubernetesResource'To filter by specific namespaces or resource types:
SELECT *
WHERE resourceType = 'AWSCustom::EKS::KubernetesResource'
AND resourceId LIKE '/kube-system/ConfigMap%'Creating Compliance Rules
Minimum Replicas for High Availability
Ensure your deployments maintain high availability by enforcing minimum replica counts:
rule kubernetes_deployment_min_replicas
when resourceType == "AWSCustom::EKS::KubernetesResource" {
# Only evaluate this rule if the Kubernetes Resource is a Deployment
when configuration.K8sResourceKind == "Deployment" {
# Ensure the Deployment has at least 2 replicas
configuration.K8sItem.spec.replicas >= 2
}
}Approved Container Registries
Enhance security by ensuring all container images come from approved registries:
let approved_registries = [
/^registry.mycorp.com\/.*/,
/^public.ecr.aws\/docker\/.*/
]
rule kubernetes_approved_registries
when resourceType == "AWSCustom::EKS::KubernetesResource" {
# Only evaluate this rule if the Kubernetes Resource is a Pod
when configuration.K8sResourceKind == "Pod" {
# Check all containers use approved registry
configuration.K8sItem.spec.containers[*] {
image IN %approved_registries
}
# Also check init containers if present
when configuration.K8sItem.spec.initContainers EXISTS {
configuration.K8sItem.spec.initContainers[*] {
image IN %approved_registries
}
}
# Check ephemeral containers if present
when configuration.K8sItem.spec.ephemeralContainers EXISTS {
configuration.K8sItem.spec.ephemeralContainers[*] {
image IN %approved_registries
}
}
}
}Finding Non-Compliant Resources
Quickly identify resources that don’t meet your compliance requirements:
SELECT
configuration.targetResourceId,
configuration.targetResourceType,
configuration.complianceType,
configuration.configRuleList
WHERE configuration.complianceType = 'NON_COMPLIANT'
AND configuration.targetResourceType = 'AWSCustom::EKS::KubernetesResource'
AND configuration.targetResourceId LIKE '/default/Pod/%'Troubleshooting Common Issues
Resources Not Being Recorded
Problem: Resources are not being recorded.
Solution: Check the CloudFormation parameters and ensure the correct resource types and namespaces are included in your configuration.
Rules Not Evaluating Correctly
Problem: Rules are not evaluating correctly.
Solution: Verify the Guard rule syntax and ensure the scope of changes is set to Resources with the correct resource type. Pay special attention to field names and data types in your rules.
Best Practices for Kubernetes Compliance
- Regularly Review: Audit your AWS Config rules quarterly to ensure they align with your organization’s evolving security and compliance policies.
- Use Conformance Packs: Group related rules and remediation actions for easier management and consistent enforcement across multiple accounts.
- Automate Remediation: Leverage AWS Systems Manager Automation documents to automatically fix non-compliant resources, reducing manual intervention and improving response time.
- Monitor Compliance Trends: Use continuous monitoring dashboards to track compliance trends over time and identify patterns in violations.
Taking Your Kubernetes Compliance Further
Ready to take control of your Kubernetes compliance? Start by implementing basic rules for replica counts and image registries, then gradually expand to cover more complex scenarios like resource limits, network policies, and pod security standards.
For more advanced configurations and troubleshooting tips, explore the AWS Config documentation and the open-source Config for Kubernetes project repository. With the right setup, you can achieve comprehensive visibility and control over your Kubernetes infrastructure while maintaining the agility that makes Kubernetes powerful.