Three Core Features
1. Self-Service Explores
| Capability | Description |
|---|---|
| Drag-and-Drop Interface | Visual query building without writing LookML or SQL |
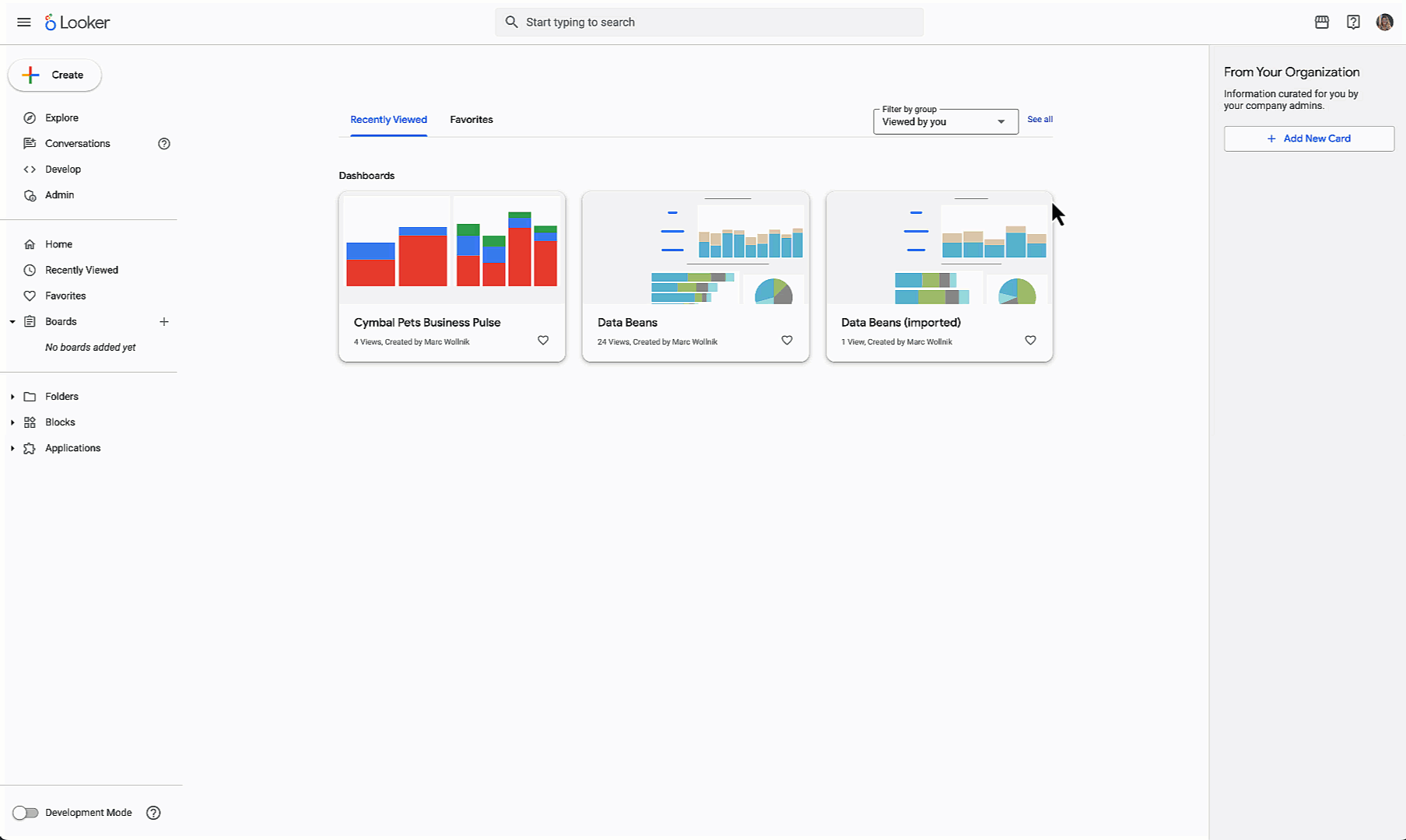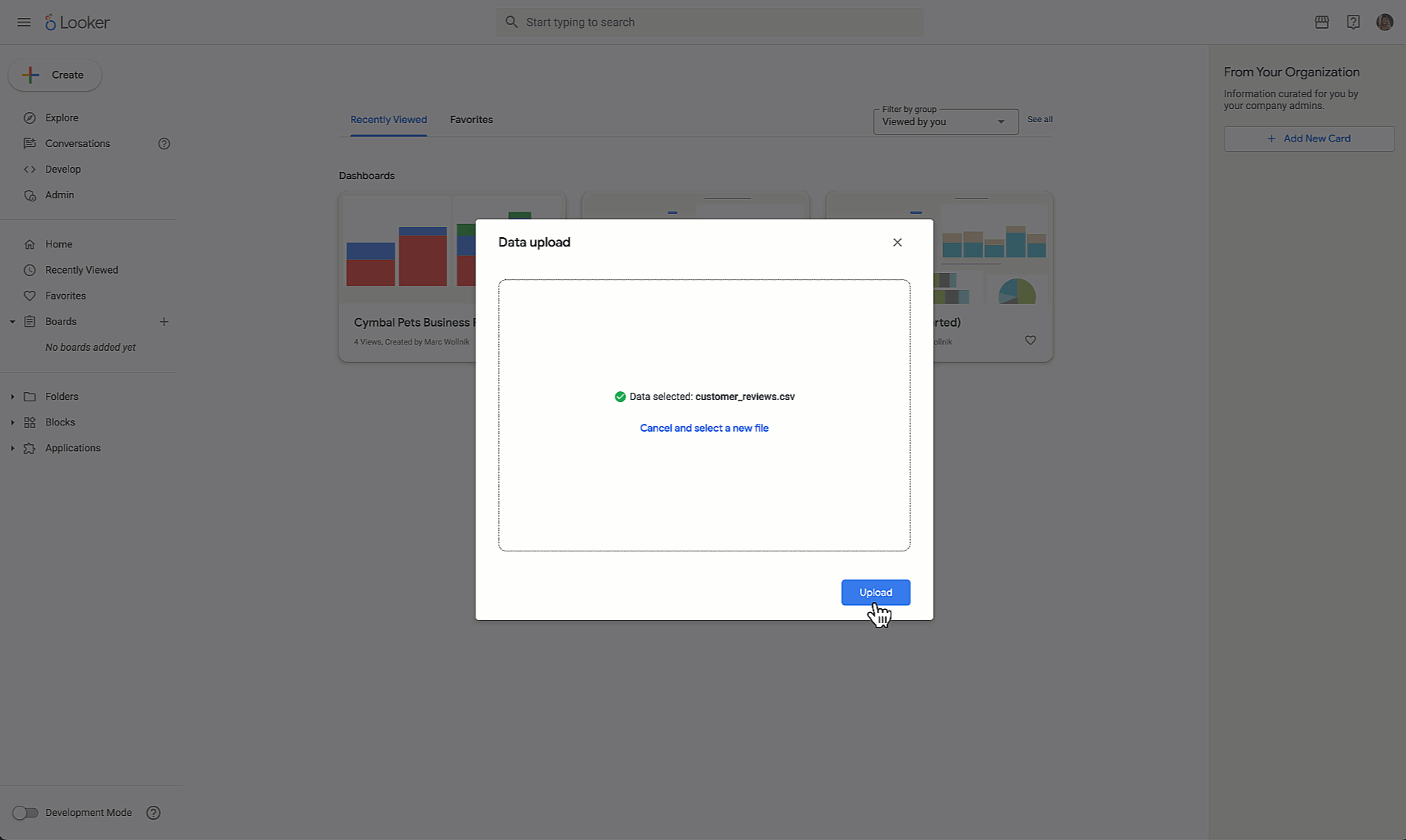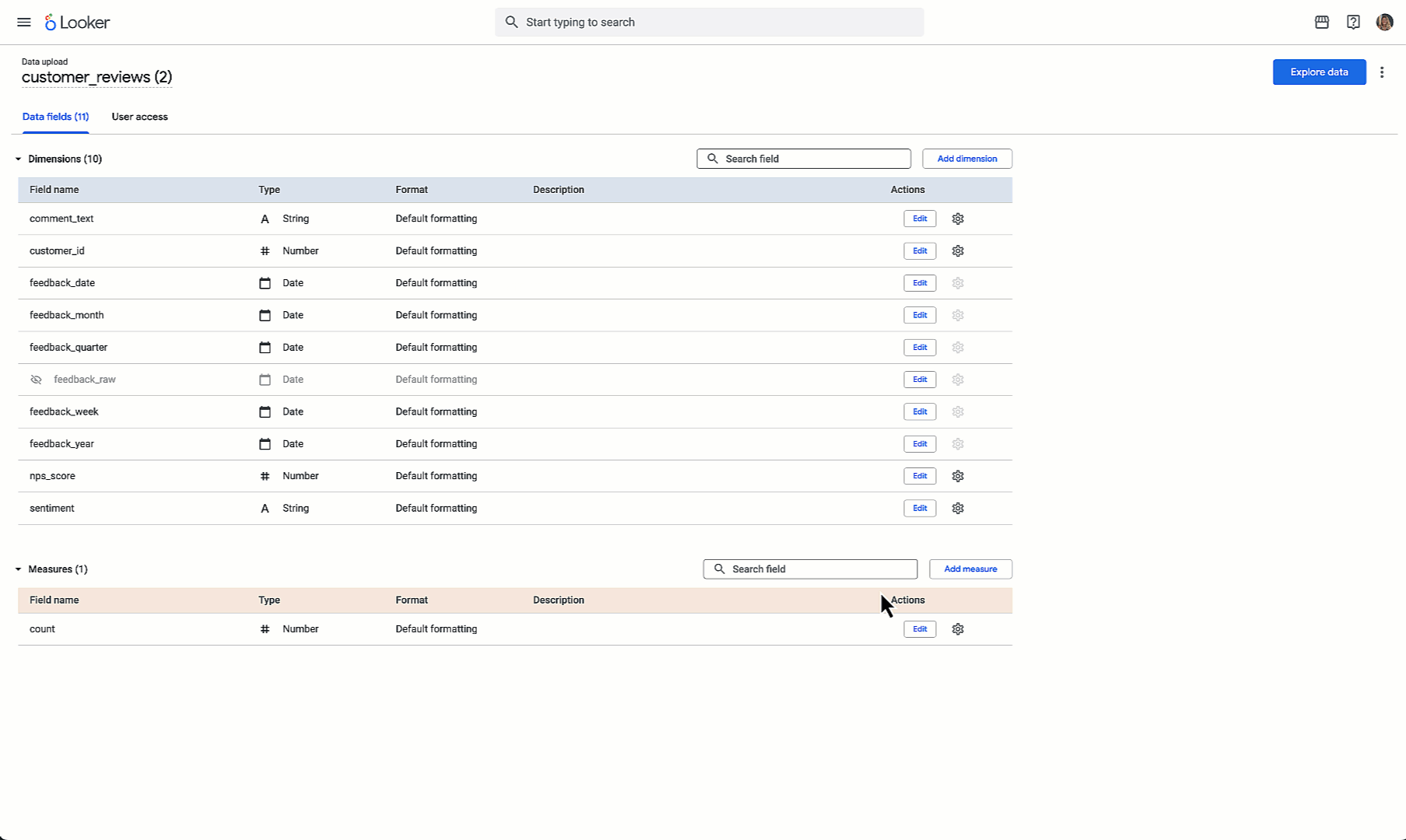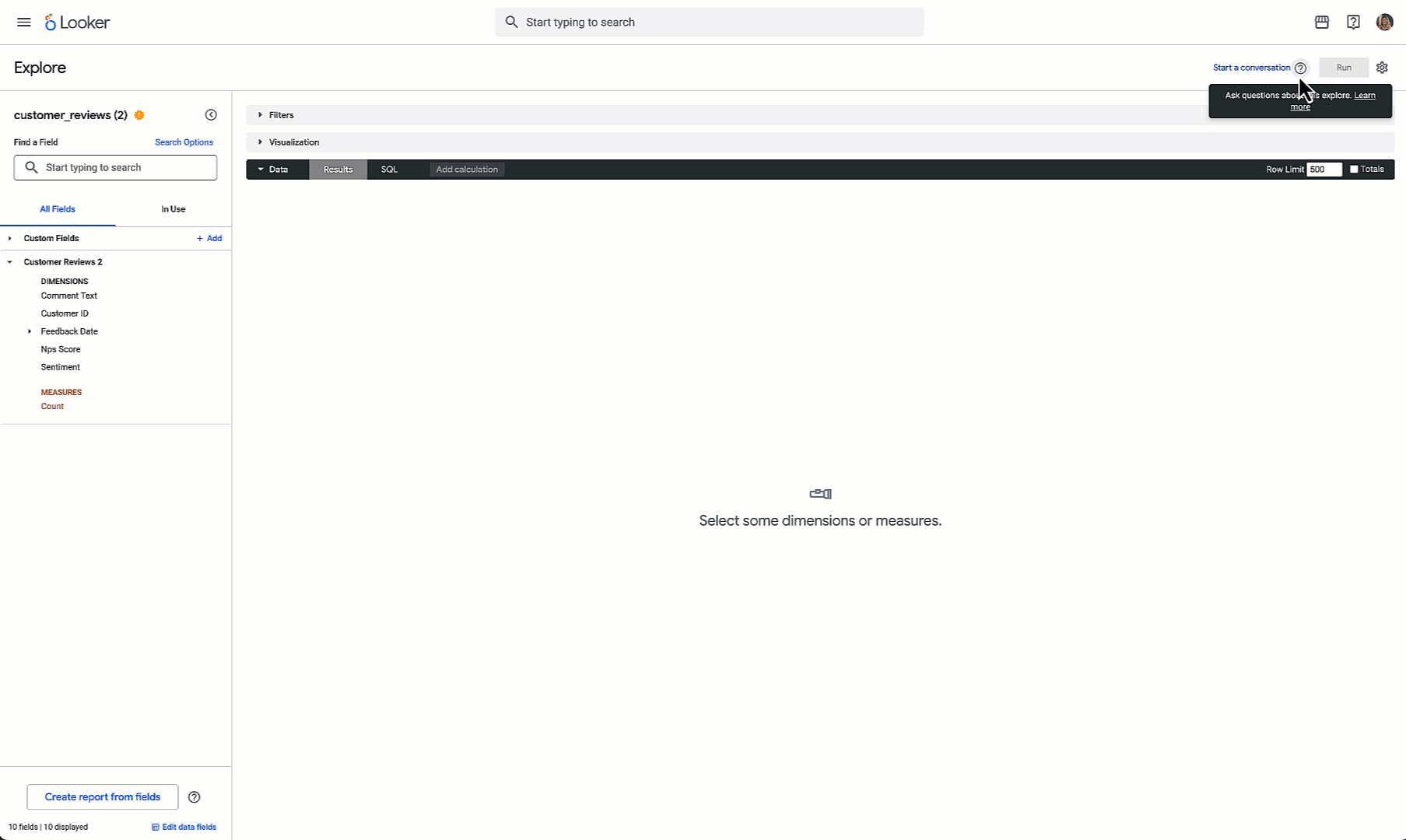
| Local File Integration | Combine uploaded CSV/Excel files with modeled Looker data |
| Data Blending | Merge external data sources with enterprise datasets |
| Ad-hoc Analysis | Experiment with data combinations without modifying data models |
Use Cases
- Market comparison: Upload competitor pricing data and compare against internal sales data
- Budget analysis: Combine departmental budget spreadsheets with actual spend from ERP systems
- Customer enrichment: Merge third-party demographic data with internal customer records
- Quick prototyping: Test data relationships before requesting formal data model changes
Administrator Controls
- Oversight of which files can be uploaded
- User permission management for upload capabilities
- File size and type restrictions
- Data governance and security policies
2. Tabbed Dashboards
| Feature | Functionality |
|---|---|
| Tab Organization | Group related visualizations into logical sections |
| Tab Management | Add, rename, and reorder tabs |
| Cross-Tab Filtering | Filters automatically apply across all tabs in dashboard |
| Unique URLs | Share direct links to specific tabs |
| PDF Export | Download entire multi-tab dashboard as single PDF |
| Scheduling | Automated delivery of complete tabbed dashboards |
Example Dashboard Structure
| Dashboard Type | Possible Tab Organization |
|---|---|
| Executive Overview | Summary → Revenue → Expenses → KPIs → Forecast |
| Sales Performance | Overview → By Region → By Product → By Rep → Pipeline |
| Marketing Analytics | Campaigns → Channels → Conversions → Attribution → ROI |
| Operations Metrics | Efficiency → Quality → Capacity → Issues → Trends |
Benefits
- Reduced cognitive load: Information organized into digestible sections
- Narrative structure: Guide users through logical story progression
- Focused sharing: Link directly to relevant tab rather than entire dashboard
- Simplified maintenance: Organize related content without creating multiple dashboards
3. Custom Themes
| Customizable Element | Options |
|---|---|
| Tile Styles | Border styles, shadows, spacing, corner radius |
| Colors | Background colors, text colors, chart palettes |
| Fonts | Typography choices, sizes, weights |
| Formatting | Number formats, date displays, alignment |
Use Cases
- Brand consistency: Match dashboards to corporate design standards
- Department customization: Finance dashboards look different from Marketing
- Client-facing reports: White-label dashboards with client branding
- Accessibility: High-contrast themes for users with visual impairments
Enabling Custom Themes
Navigate to Admin → Labs page and enable Internal dashboard theming. Note that this applies only to dashboards consumed within the Looker application, not embedded dashboards.
Problem These Features Solve
Traditional BI Bottlenecks
| Challenge | Looker Solution |
|---|---|
| Technical Expertise Required | Drag-and-drop interface reduces need for SQL/LookML knowledge |
| External Data Integration | Self-service file uploads enable quick data blending |
| Dashboard Complexity | Tabs organize information into manageable sections |
| Generic Appearance | Custom themes align with organizational branding |
| Data Team Backlog | Business users can explore data without IT requests |
Target Users
Who Benefits Most
| User Type | Primary Benefit |
|---|---|
| Business Analysts | Ad-hoc analysis without waiting for data team support |
| Marketing Teams | Blend campaign data with CRM and web analytics |
| Finance Users | Combine budget spreadsheets with actuals from ERP systems |
| Sales Operations | Merge external market data with internal sales metrics |
| Dashboard Creators | Organized, branded dashboards without custom development |
| Executives | Intuitive navigation through complex information |
Availability and Access
Current Status
- Release stage: Public Preview
- Availability: All Looker customers can enable features
- Documentation: Self-service Explores guide
- Feedback: Users encouraged to provide input to Looker team during preview
Prerequisites
- Active Looker license
- Administrator access to enable features (for admin-level settings)
- User permissions configured by administrators
Comparison to Competitors
Self-Service BI Landscape
| Platform | Self-Service Approach | Key Differentiator |
|---|---|---|
| Looker | Drag-and-drop + modeled data governance | Combines flexibility with enterprise data modeling |
| Tableau | Visual analytics with prep builder | Strongest data visualization capabilities |
| Power BI | Excel-familiar interface + Power Query | Deep Microsoft ecosystem integration |
| Qlik | Associative engine for exploration | Unique data discovery through associations |
| Thoughtspot | Natural language search | Search-driven analytics interface |
Implementation Considerations
Governance Concerns
- Data quality: User-uploaded files may contain errors or inconsistencies
- Security: Sensitive data in spreadsheets could bypass normal controls
- Version control: Tracking which file version was used for analysis
- Audit trails: Monitoring who uploads what data and when
- Storage limits: Managing accumulated uploaded files
Best Practices
- Clear policies: Define acceptable file upload use cases and restrictions
- User training: Educate users on data quality and security implications
- Regular audits: Review uploaded files and usage patterns
- Graduated permissions: Start with limited users before broad rollout
- Documentation: Maintain guidelines for dashboard organization and theming
Success Metrics
| Metric | What to Track |
|---|---|
| Adoption Rate | Number of users creating self-service Explores |
| Request Reduction | Fewer data team tickets for ad-hoc analysis |
| Dashboard Engagement | Time spent in tabbed dashboards vs. traditional dashboards |
| User Satisfaction | Feedback on ease of use and feature utility |
| Time to Insight | Reduced time from question to answer |
Limitations and Trade-offs
What These Features Don’t Solve
- Data modeling complexity: Still requires LookML expertise for underlying data models
- Performance optimization: User-created explores may not be as optimized as modeled queries
- Advanced analytics: Complex statistical analysis still requires specialized tools
- Real-time data: Depends on underlying data refresh schedules
- Embedded dashboards: Custom themes only apply to internal Looker application, not embedded views
When Traditional Approaches Are Better
- Highly complex data transformations requiring ETL pipelines
- Mission-critical dashboards requiring guaranteed performance
- Scenarios where data governance must be absolute
- Cases where user-uploaded data creates compliance risks
Looker’s new self-service features—drag-and-drop Explores, tabbed dashboards, and custom themes—reduce technical barriers to data analysis while maintaining enterprise-grade data governance. These updates address common BI challenges: long wait times for data team support, complex dashboard navigation, and generic appearances that don’t align with organizational branding.
The self-service Explores feature tackles a persistent problem: business users needing to combine external data (spreadsheets, third-party sources) with internal enterprise data. Previously, this required either data engineering work or separate analysis in tools like Excel. Now users can upload files and blend them with modeled Looker data while administrators retain oversight and control.
Tabbed dashboards solve the cognitive overload problem when dashboards become too complex. By organizing related visualizations into logical sections with cross-tab filtering, Looker enables clearer data storytelling and more focused sharing through tab-specific URLs.
Custom themes address adoption challenges by allowing organizations to make dashboards feel like part of their existing systems rather than a separate analytics tool. This seemingly cosmetic change can significantly impact user engagement and adoption rates.
However, these features don’t eliminate the need for data expertise. Underlying data models still require LookML knowledge, performance optimization remains a specialist task, and governance challenges increase when users can upload arbitrary files. Organizations should implement clear policies, user training, and regular audits to prevent data quality and security issues.
The Public Preview status means features may evolve based on user feedback. Organizations should test thoroughly before relying on these capabilities for critical workflows, and participate in feedback channels to shape final implementation.
For organizations with significant data team backlogs and users who understand their data but lack technical SQL/LookML skills, these features can meaningfully accelerate insight generation. Success depends on balancing self-service flexibility with appropriate governance controls.