Traditional cybersecurity measures, designed for predictable enterprise IT environments, often fall short when protecting the dynamic and data-intensive pipelines that power modern AI systems. The unique architecture of AI applications—spanning from data ingestion and model training to inference endpoints—creates novel opportunities for attackers that standard security tools may not recognize. This gap has given rise to a specialized discipline: AI threat intelligence.
AI threat intelligence is the practice of identifying, tracking, and mitigating threats that specifically target AI and machine learning systems. It moves beyond the scope of conventional threat feeds, which typically focus on malware signatures, phishing campaigns, or network intrusions. Instead, it concentrates on the distinct ways adversaries can compromise AI models, poison training data, exploit underlying cloud infrastructure, and abuse the automated identities that connect these components. Understanding these AI-centric attack vectors is no longer optional; it is a critical requirement for any organization deploying AI in production.
The core challenge is that AI system failures are rarely the result of a single, isolated vulnerability. More often, they stem from a chain of interconnected weaknesses, such as an exposed cloud storage bucket, a hardcoded credential in a public code repository, and an overly permissive service account. This article will explore the key pillars of AI threat intelligence, breaking down the primary risk categories and explaining how security teams can move from passive awareness to an actionable defense strategy that protects their entire AI ecosystem.
Effective AI threat intelligence provides visibility into the specific ways attackers target the components of an AI stack. Rather than focusing on abstract model-level threats, it zeroes in on observable and preventable security failures in the infrastructure, identities, and data pipelines that support AI workloads. By understanding these key areas, security teams can better anticipate and defend against real-world attack techniques.
Vulnerabilities in AI Infrastructure
AI models do not run in a vacuum; they depend on a complex stack of software and hardware, including specialized servers, container orchestration platforms, and data processing frameworks. Vulnerabilities in these infrastructure components represent a significant risk. For instance, a remote code execution flaw in an AI serving framework like NVIDIA Triton Inference Server could allow an attacker to gain control of the underlying host, potentially leading to model theft, data exfiltration, or further lateral movement within the network. AI threat intelligence must track these CVEs and provide context on how they can be exploited in a production AI environment.
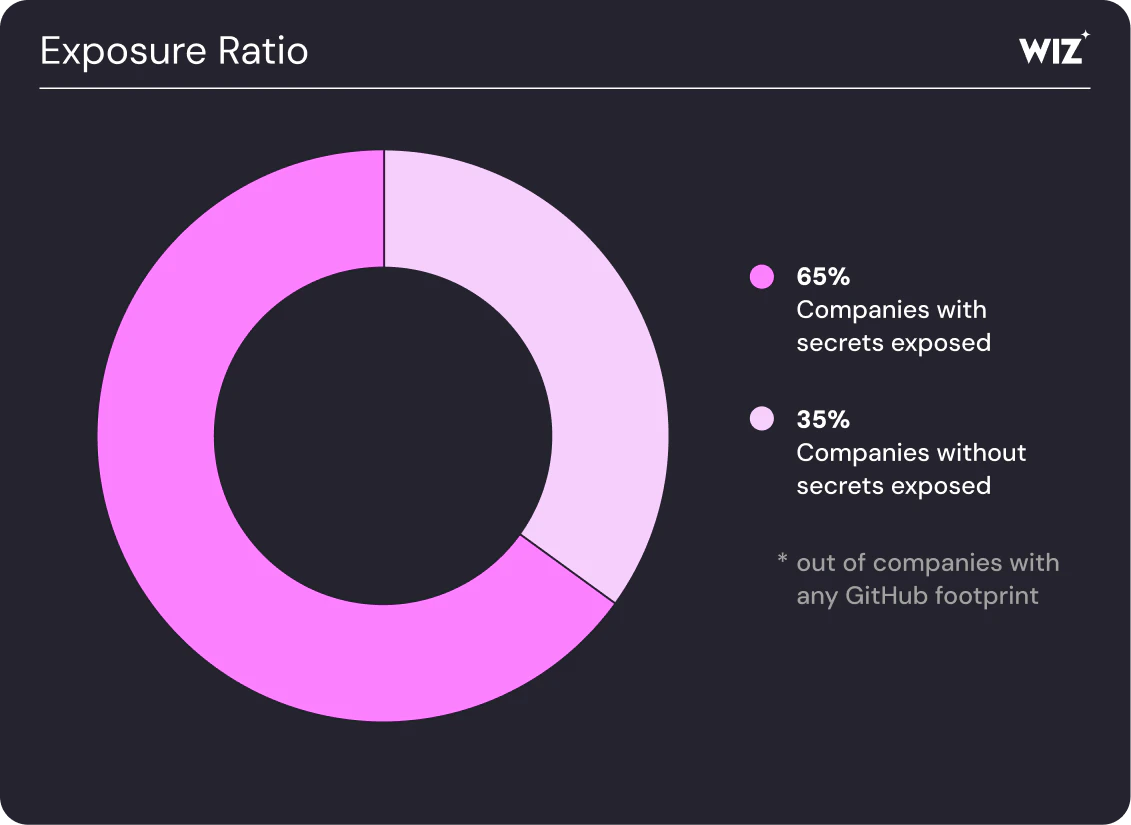
Leaked Secrets and Exposed Credentials
The development and deployment of AI systems heavily rely on automation, which is powered by non-human identities such as API keys, service account credentials, and access tokens. According to research from firms like Wiz, a common point of failure is the accidental exposure of these secrets in public code repositories. A developer might inadvertently commit a key that grants access to a cloud AI service or a sensitive data store. Attackers continuously scan public platforms like GitHub for such leaks, which can provide a direct path to compromise high-value AI assets. This risk is highlighted in standards like the OWASP Top 10 for Large Language Model Applications.
Abuse of Non-Human Identities
Beyond accidental leaks, the identities used to automate AI pipelines are themselves a primary target. These non-human identities often require broad permissions to access data, train models, and deploy endpoints. If an attacker compromises a service account, they inherit all of its permissions. A major risk is the use of over-privileged identities, which grant far more access than necessary. For example, a single compromised identity could potentially have permissions to read sensitive training data, modify a production model, and exfiltrate the results, all while appearing as legitimate automated activity.
Insecure Data Access and Pipelines
Data is the lifeblood of any AI system, making its protection paramount. AI threat intelligence monitors how data is stored, accessed, and processed throughout its lifecycle. This includes identifying misconfigured cloud storage buckets containing sensitive training datasets, overly permissive access controls on data lakes, and unsecured data transit between different stages of the MLOps pipeline. Attackers can target these weaknesses to steal proprietary data, inject malicious information to poison a model (a data poisoning attack), or disrupt the availability of critical AI services.
Threat intelligence is only valuable when it becomes actionable. For AI systems, this means connecting isolated security findings into a coherent narrative of risk. A single leaked key is a problem, but its severity increases dramatically when that key belongs to an over-privileged identity with access to a production database containing sensitive customer information. Modern security platforms, often categorized as AI Security Posture Management (AI-SPM), use a security graph to map these relationships. According to Wiz, this approach allows teams to visualize and prioritize realistic attack paths, transforming a flood of low-context alerts into a focused list of critical risks that require immediate attention.
As AI becomes more deeply integrated into business processes, securing these systems requires a specialized and context-aware approach. AI threat intelligence shifts the focus from generic cyber threats to the specific vulnerabilities, misconfigurations, and attack vectors unique to the AI ecosystem. By concentrating on infrastructure security, credential management, identity permissions, and data pipeline integrity, organizations can build a more resilient defense. Ultimately, the goal is to move beyond theoretical risks and implement an actionable security strategy that understands how different weaknesses connect, enabling teams to proactively dismantle potential attack paths before they can be exploited.
Follow us on Bluesky , LinkedIn , and X to Get Instant Updates