Tata Motors, a globally recognized Indian automotive manufacturer, experienced a significant data breach in 2023, exposing over 70 terabytes of sensitive information. This incident underscores the ever-present threat of cyberattacks, even against large and established organizations. The breach was attributed to several security oversights, including exposed Amazon Web Services (AWS) credentials, easily decrypted keys, an unsecured Tableau backdoor, and an unprotected API key. The combination of these vulnerabilities created a substantial risk to customer data, financial records, and critical administrative systems.
AWS Keys Exposed on E-Dukaan Marketplace
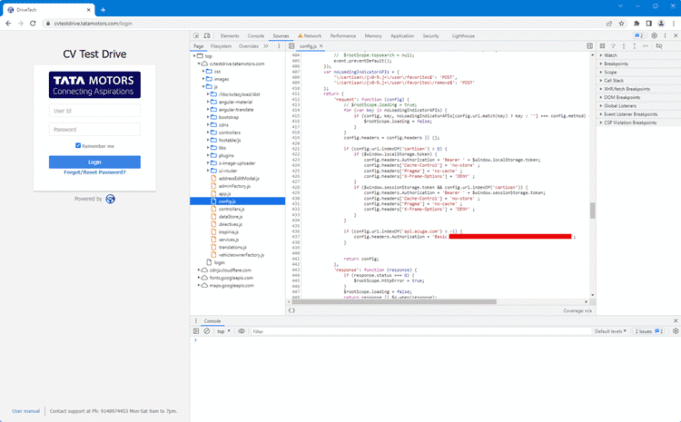
A primary vulnerability originated from E-Dukaan, Tata Motors’ e-commerce platform for spare parts. Security researchers discovered AWS access keys hardcoded in plaintext within the website’s source code. This allowed unrestricted access to Amazon S3 buckets, revealing sensitive information such as complete customer database backups, market intelligence reports, hundreds of thousands of invoices with personal identification numbers, and approximately 40 gigabytes of administrative order reports.
The risk was amplified because these keys were used to download a file containing tax codes. The FleetEdge fleet management platform also contained AWS credentials, initially appearing encrypted. However, the encryption was client-side only, allowing anyone with basic technical knowledge to easily extract and decrypt the keys. This provided a false sense of security, as both the encrypted data and decryption keys resided on the same system.
Impact of Exposed Credentials
The exposed credentials granted access to approximately 70 terabytes of historical fleet intelligence data dating back to 1996, stored in a single bucket. Additionally, write access to multiple websites was granted, posing a risk of malware injection.
Flawed Authentication Systems on E-Dukaan
The E-Dukaan platform also contained hardcoded Tableau credentials in source code comments. However, a more critical issue was the implementation of a flawed authentication system. This vulnerable code allowed users to obtain “trusted tokens” using only a username and site name, completely bypassing password requirements. Security researchers demonstrated the ability to impersonate any user on the system, including server administrators, gaining complete control over Tableau dashboards. This access provided control over countless internal projects, financial reports, and dealer-specific information.
This authentication bypass effectively meant that anyone with access to the website’s source code, even without authorization, could gain administrative privileges. The test drive management system relied on an Azuga API key, which was also hardcoded into JavaScript source code. This exposed credential provided direct access to the fleet management platform, potentially allowing unauthorized individuals to track vehicle locations and monitor test drive operations in real time.
Dangers of Client-Side Credential Storage
The incident highlighted a broader pattern of developers incorrectly treating client-side code as a secure location for sensitive credentials. The practice of embedding API keys, AWS keys, and other sensitive information directly into client-side code is a significant security risk, as it makes these credentials easily accessible to attackers.
Key Vulnerabilities
* Hardcoding credentials
* Client-side encryption
* Authentication system flaws
Tata Motors’ Response to the Breach
The security issues were reported to Tata Motors through India’s Computer Emergency Response Team (CERT-IN). However, the remediation process proved to be slow and frustrating. While Tata Motors acknowledged receipt of the report and claimed to have addressed the issues, follow-up verification revealed that only 2 out of 4 issues had been resolved. AWS keys remained active on both websites. It took until January 2024 for the company to fully revoke the exposed credentials after months of clarifying specific remediation steps.
The delay in fully addressing the vulnerabilities raised concerns about Tata Motors’ incident response capabilities and the effectiveness of their internal security protocols. The incident also highlighted the importance of regular security audits and penetration testing to identify and address potential vulnerabilities before they can be exploited by attackers.
Impact of the Data Breach
This data breach serves as a stark reminder that even major international corporations can fall victim to fundamental security mistakes. The vulnerabilities demonstrated the dangers of hardcoding credentials, using ineffective client-side encryption, and implementing authentication systems with serious logical flaws. For customers of Tata Motors, the breach raised significant questions about the company’s data protection standards.
Key Security Practices
The incident underscores the critical need for organizations to prioritize security best practices, including:
* Regular security audits
* Robust access controls
* Strong encryption
* Prompt incident response
* Employee training on security awareness
By implementing these measures, organizations can significantly reduce their risk of experiencing a similar data breach and protect their sensitive data from unauthorized access. The Tata Motors incident also highlights the importance of third-party risk management, as many of the vulnerabilities were found in systems provided by external vendors. Organizations must ensure that their vendors adhere to the same security standards and practices as they do.